Programming in Python
BEES 2023

Agenda
- Strings:
- White space characters
- String operators
- String functions
- Slicing
- Immutability
- String comparison
- For loops
- In operator
- Lists
0
Advanced issues found▲
String data type
- Text is represented in programs by the string data type
- A string is an immutable sequence of characters enclosed within quotation marks (") or apostrophes (').
- Example:
- ‘This is a sample sentence.’
- “2x2=4”
whitespace characters
String indexing
greet = "Hello Bob"
print(greet[0])
print(greet[0], greet[2], greet[4])
x = 8
print(greet[x - 2])
print(greet[-1])
print(greet[-3])
print(greet[50]) # Error
print(greet[-(len(greet)+1)]) # This throws an error,
# it implies a character before the start of the string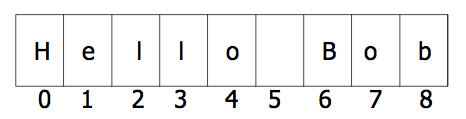
String length function
-
The length of a string is given by the "len()" function
s = "A long string"
print(len(s))
# The empty string case
s = ""
print(len(s))
# A String with whitespace character
s = "\t"
print(len(s))Character is just another String
s = "A long string"
# Realise that a character is just another string in Python
# In some languages, like C/C++, individual characters
# are not strings but have a different type, but Python
# treats them as a single character string
print(type(s[0])) # Prints str
print(len(s[0])) # Prints 1
String slicing
# Beyond indexing, you can slice strings to create substrings
greet = "Hello Bob"
print(greet[0:3]) # The 'prefix' substring of the first 3 characters
print(greet[3:3]) # The interval [3, 3) is empty
print(greet[5:8])
# Negative length strings?
print(greet[6:0]) # If the second index occurs before the first index it won't
# throw an error, just make a zero length (empty) string
print(greet[:5]) # This is the same as greet[0:5]
# greet[:n] is called a prefix of greet, where n is in [0, len(greet))
print(greet[5:]) # This is the same as greet[5:9]
# greet[n:] is called a suffix of greet, where n is in [0, len(greet))
print(greet[:]) # This is just the whole string, allowing you to make
# a copy of the stringString immutability
- Strings are immutable
- You cannot edit a string, you can only make new strings by copying them
s = "Strings can't be changed"
# This doesn't work
s[0] = 's'
# To make s lower case you could instead do:
s = 's' + s[1:]
print(s)string comparison
in operator
for loops on strings
Example: removing vowels
Lists
- An ordered sequence of information, accessible by index
- A list is denoted by sequence brackets "[ ]"
- A list contains elements
- Usually homogeneous
- Can contain mixed types
- List elements can be changed, so a list is mutable
List functions - review
Lists are mutable
- Lists are mutable
- Assigning to an element at an index changes the value
- L is now [2, 5, 3], note this is the same object L
L = [2, 1, 3]
L[1] = 5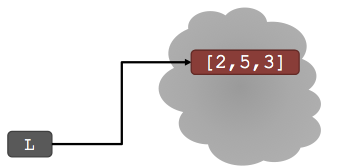
List mutability
Conversion and nesting
aliasing
0
Advanced issues found▲
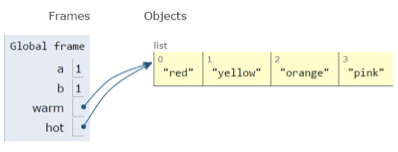
- "hot" is an alias for "warm" - changing one changes the other
- For example, here "append" has a side effect
a = 1
b = a
print(a)
print(b)
warm = ['red', 'yellow', 'orange']
hot = warm
hot.append('pink')
print(hot)
print(warm)
cloning
0
Advanced issues found▲
- Create a new list and copy every element using
cool = ['blue', 'green', 'gray']
chill = cool[:]
chill.append('black')
print(chill)
print(cool)
chill = cool[:]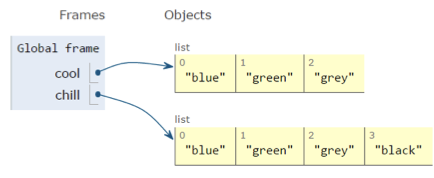
lists of lists of lists of ...
0
Advanced issues found▲
- We can have nested lists
warm = ['yellow', 'orange']
hot = ['red']
brightcolors = []
brightcolors.append(warm)
brightcolors.append(hot)
print(brightcolors)
# [['yellow', 'orange'], ['red']]
hot.append('pink')
print(hot)
# ['red', 'pink']
print(brightcolors)
# [['yellow', 'orange'], ['red', 'pink']]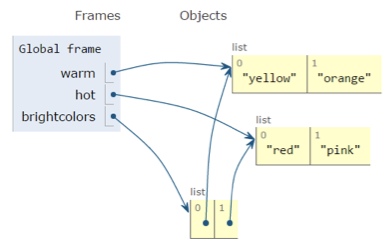
Questions?

BEES 2023 - Lecture 6
By Narges Norouzi
BEES 2023 - Lecture 6
- 460



