Lecture 10

fall 2018
Narges Norouzi
Introduction to inheritance
Class Hierarchies
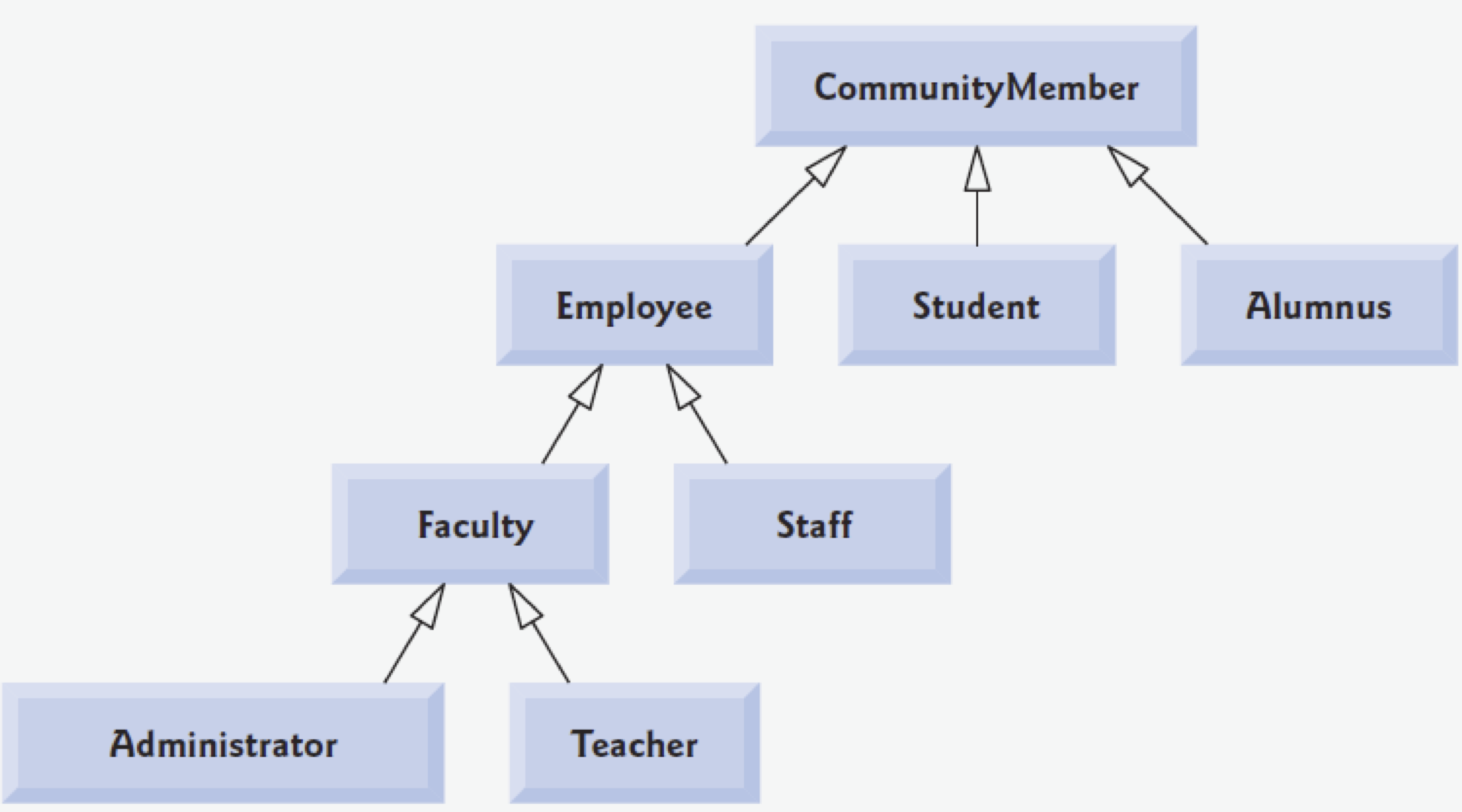
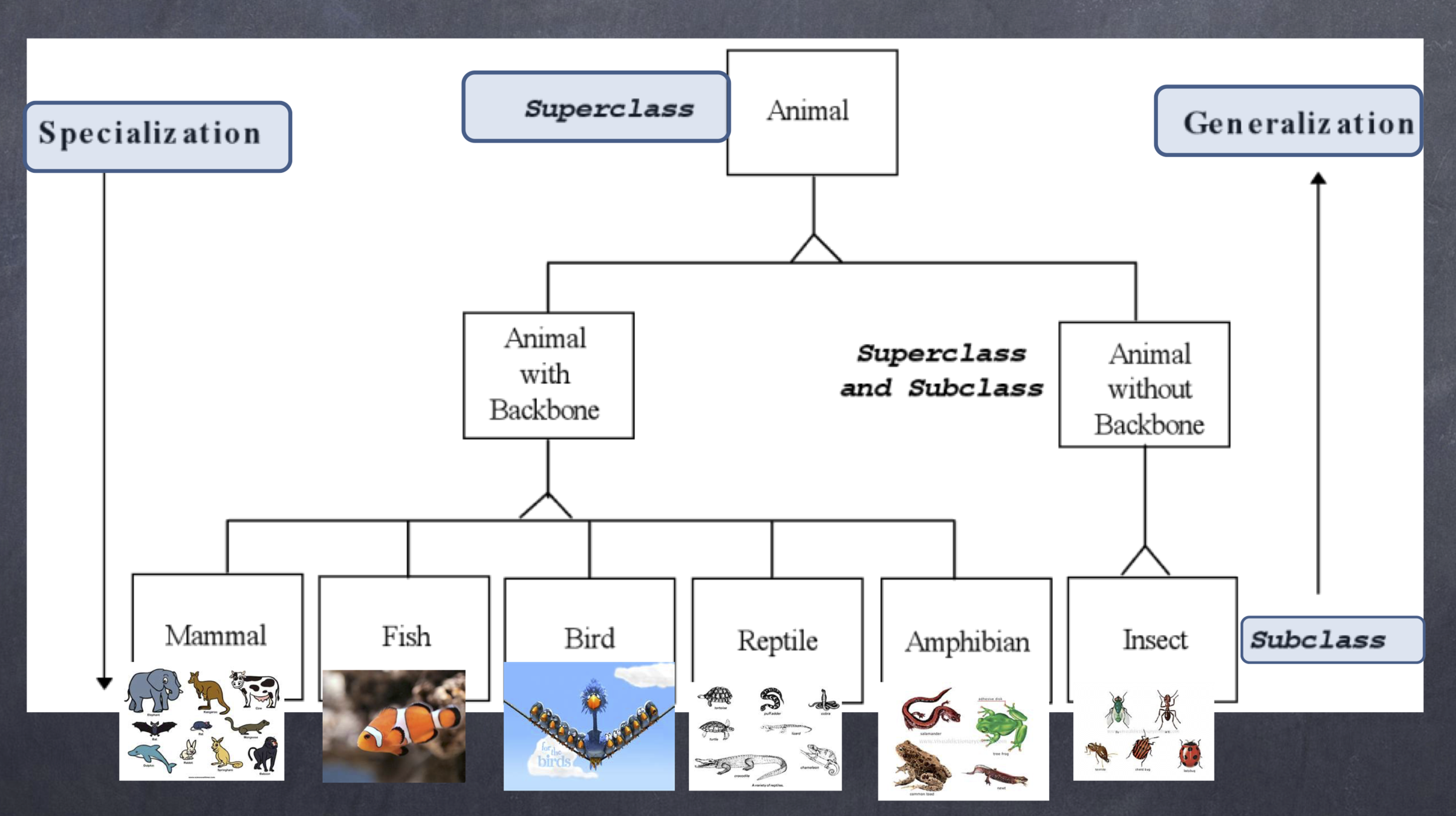
Terminology
-
Key points:
-
Inheritance is about hierarchical abstraction
-
Inheritance is about is-a relationship
-
Inheritance is about common attributes
-
Inheritance

Inheritance In java
class implementation
-
Faculty is inherited from Employee
-
How do you implement Employee class?
-
How do you implement Faculty class?
public class Employee{
String name;
double salary;
String getName(){
return this.name;
}
String getSalary(){
return this.salary;
}
void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
void setSalary(double salary){
this.salary = salary
}
}public class Faculty{
//Employee properties
String name;
double salary;
String getName(){
return this.name;
}
String getSalary(){
return this.salary;
}
void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
void setSalary(double salary){
this.salary = salary
}
//Faculty-specific properties
Course[] courses;
Course[] getOfferedCourses(){
return this.courses;
}
int getNumOfCourses(){
return this.courses.length;
}
}faculty & employee
-
Faculty is inherited from Employee
-
Faculty extends Employee
-
Attributes and behaviors of Employee will be inherited by Faculty
-
Inheritance provides code reuse
faculty class again
public class Faculty extends Employee{
/* We will inherit properties of Employee class,
so there is no need to re-write them here. */
//Faculty-specific properties
Course[] courses;
Course[] getOfferedCourses(){
return this.courses;
}
int getNumOfCourses(){
return this.courses.length;
}
}class hierarchy
-
Direct superclass
-
Inherited explicitly (one level up hierarchy)
-
-
Indirect superclass
- Inherited two or more levels up hierarchy
-
Multiple inheritance
- Inherits from multiple super classes
- Java does not support multiple inheritance
subclasses may ...
-
Add new functionality New members
-
Use inherited functionality Software reuse
-
Override inherited functionality Change parent methods


Zybooks chapters we covered
-
Chapter 10: Inheritance
-
Sections 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4
-