Beginning Programming in Python
Fall 2019

Agenda
- A couple of simple list algorithms:
- Linear search
- Binary search
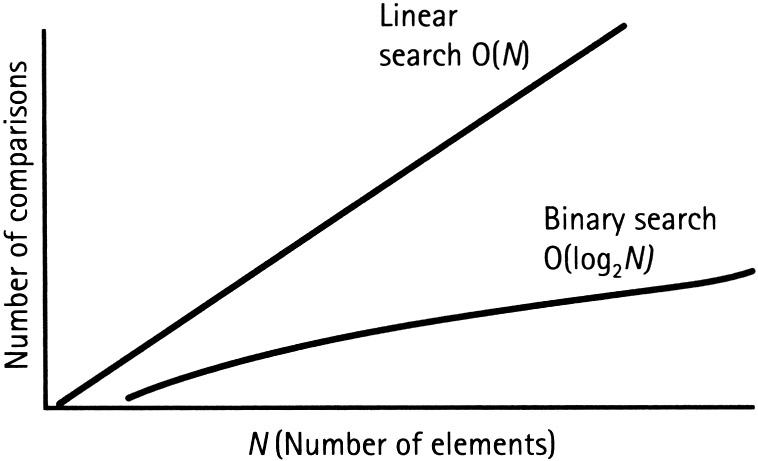
- A very brief introduction to runtime analysis and Big-O Notation
- Dictionaries
- Set
Linear search
- Linear search or sequential search is a search method for finding an element within a list
- It sequentially checks each element of the list until a match is found or the whole list has been searched
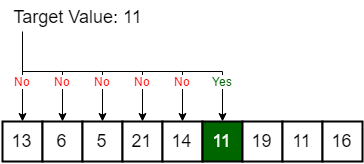
Linear search example
Binary search
-
In binary search, for a sorted list, we start from the middle of the list and then check if the middle word is less than, equal to or greater than the search query string.
-
Based on the result we can generally halve the size of the search, and so recursively solve the problem.
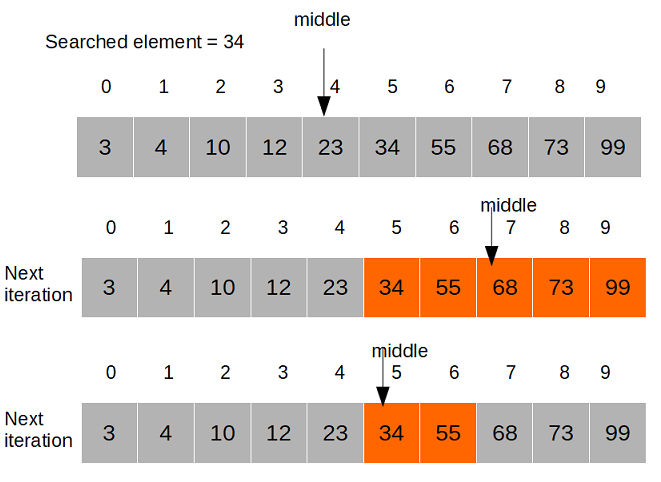
binary search example
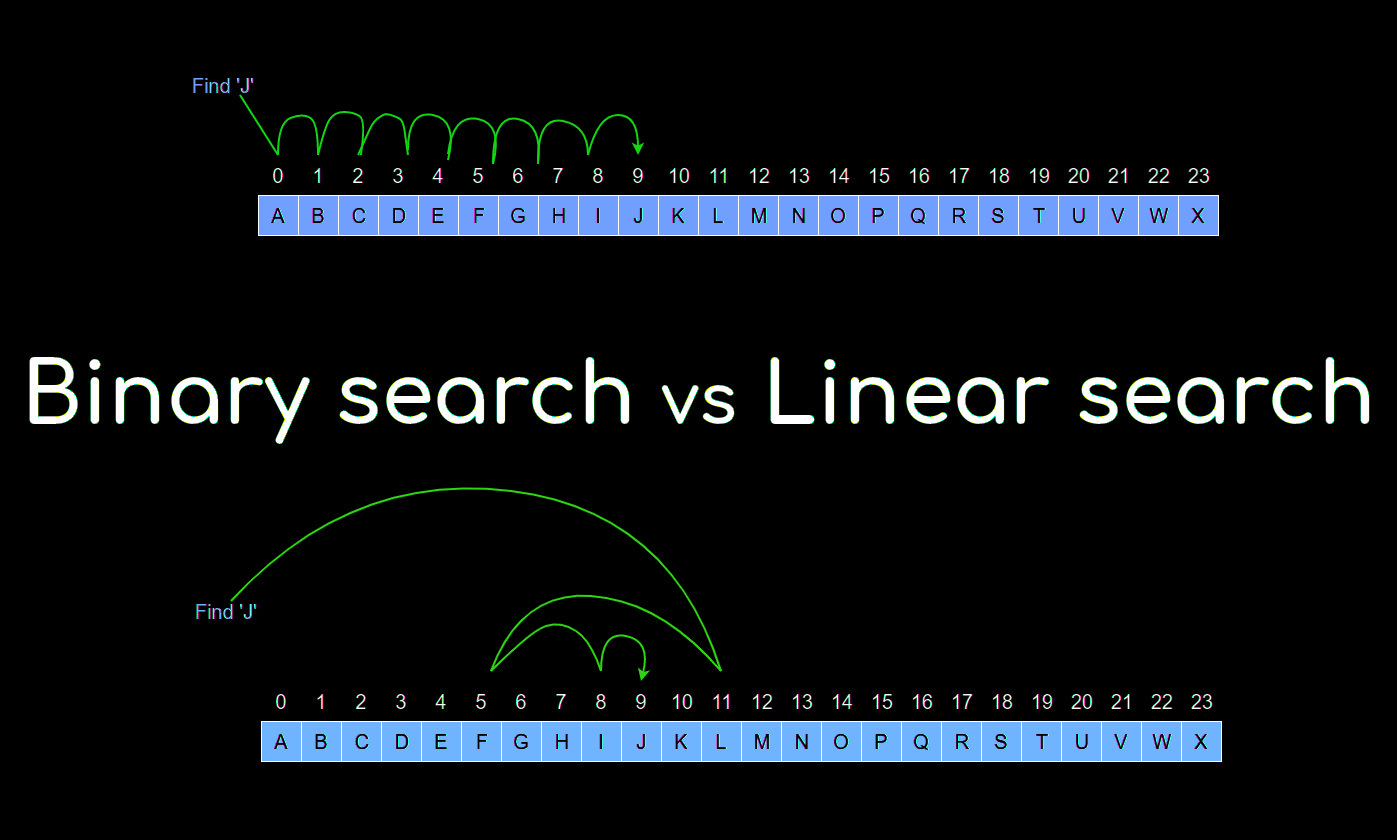
Linear vs binary search
dictionaries
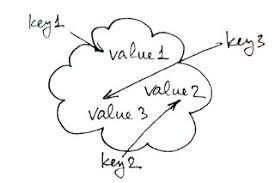
dictionary
0
Advanced issues found▲
- Dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs
- Each value can be accessed using its key
- Key can be any immutable object
eng2sp = {}
eng2sp["one"] = "uno"
eng2sp["two"] = "dos"
sp2eng = {"uno":"one", "dos":"two"}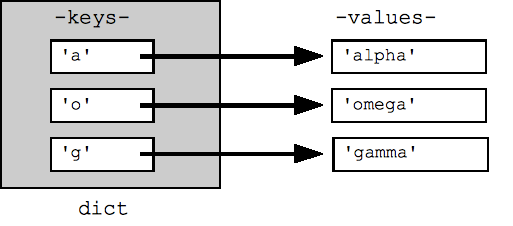
practice with dictionary
5 minutes break!
why use dictionaries?
- Convenient
- Fast
- The cost of looking up a key in the dictionary is O(1) comparing to searching a list in O(N)
- Removal and update operations are also O(1)
word counting
sets
set
0
Advanced issues found▲
- Set is a collection of unique objects
- Objects in set are not ordered
x = set(["Internet", "Radio", "TV"])
print(x)
# Prints {'Internet', 'TV', 'Radio'}
y = {"Internet","Radio","Internet"}
print(y)
# Prints {'Internet', 'Radio'}set example
Lecture 12 challenge
Questions?

CSE 20 - Lecture 12
By Narges Norouzi
CSE 20 - Lecture 12
- 1,527



