Lecture 8

Fall 2018
Narges Norouzi
Recap
- Strings
- Creation
- Methods
- Characters
- Methods
- ASCII Encoding
Object Oriented Programming
Introduction to OOP
-
Objectives:
-
Know the difference between functional programming and OOP
-
Know basic terminology in OOP
-
OOP Design
-
Structured vs. oo programming
Structured Programming:
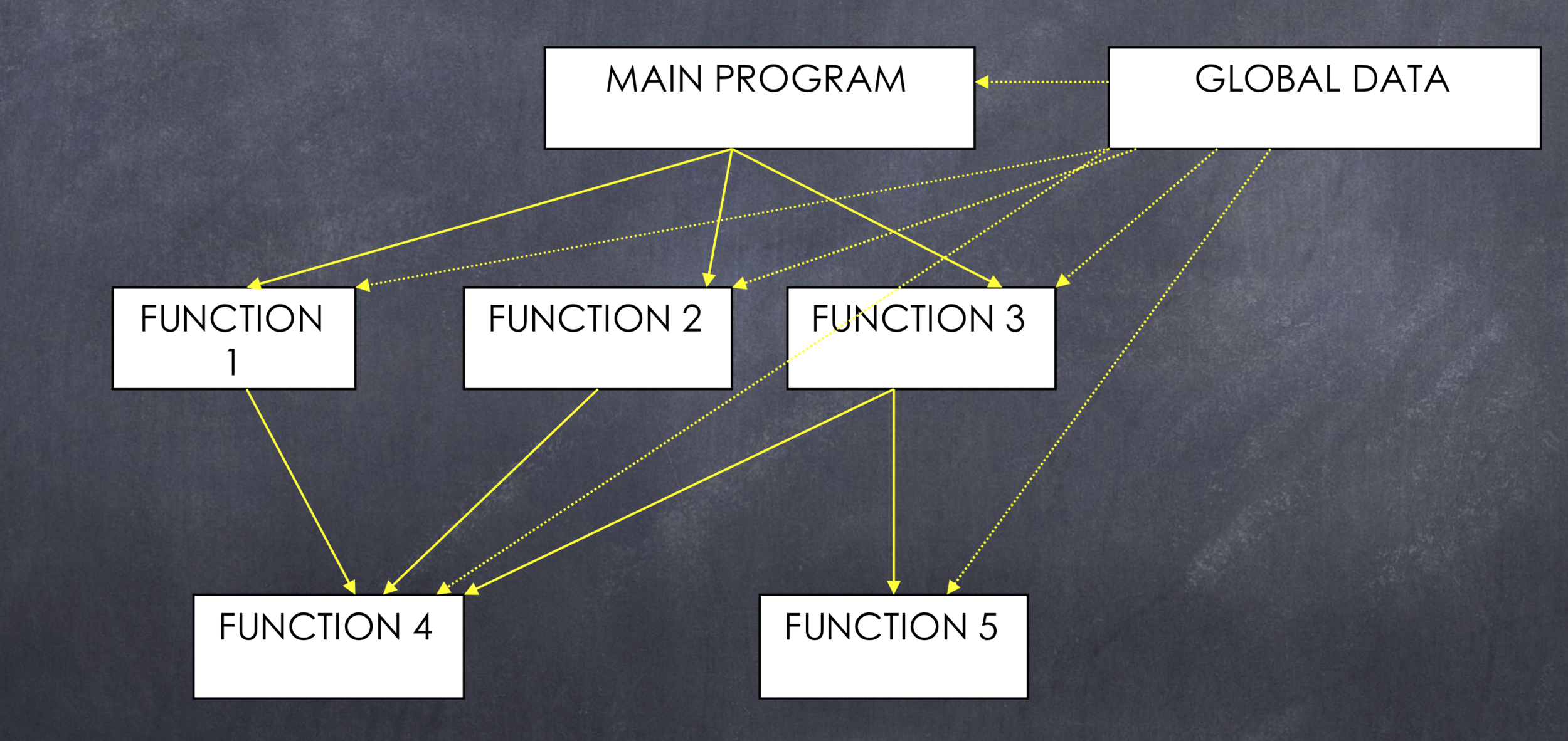
structured programming
-
Using function
-
Function & program is divided into modules
-
Every module has its own data & functions which can be called by other modules.
-
Object-Oriented approach
-
OO approach goes one step further
-
Lets the programmer represent problem space elements
-
The elements in the problem space and their representations in the solution space are referred to as "objects"
OO Programming
-
Objects have both data and methods
-
Objects send and receive messages to invoke actions
-
Objects of the same class have the same data elements and methods
-
Key idea in object-oriented programming:
-
The real world can be accurately described as a collection of objects that interact.
-
Object Oriented Programming
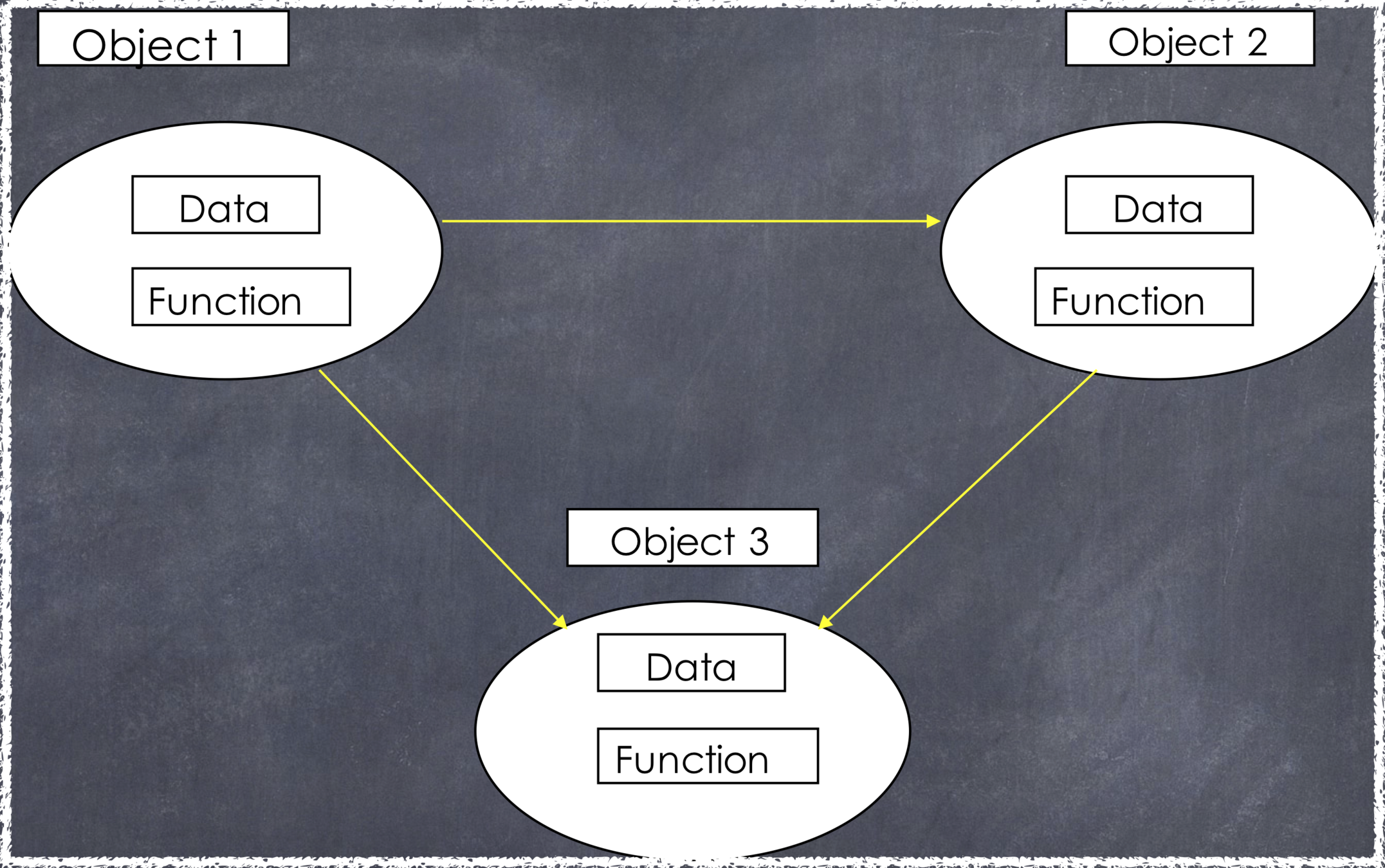
Oebjects
-
An object has:
-
state - descriptive characteristics
-
behaviors - what it can do (or what can be done with it)
-
-
Bank Account object:
-
state: account number and current balance
-
behaviors: ability to make deposits and withdrawals
-
-
Note that the behavior of an object might change its state
Classes
-
An object is created using a class
-
A class is the blueprint of an object
-
The class uses methods to define the behaviors of the object
-
A class represents a concept in problem domain
-
Multiple objects can be created from the same class
-
The class that contains the main method of a Java program represents the entire program
example: a rabbit
-
You could (in a game, for example) create an object representing a rabbit
-
It has data:
-
How hungry it is
-
How frightened it is
-
Where it is
-
-
And methods:
-
eat, hide, run, dig
-

what's a class made of?
-
Members of a class:
-
Attributes or Fields (instance variables, data)
-
For each instance of the class (object), values of attributes can vary, hence they are instance variables
-
-
Methods (instance methods)
-
-
Person class
-
Attributes: name, address, phone number
-
Methods: change address, change phone number
-
-
Alice object
-
Name is Alice, address is ...
-
Example of a class

class as an object factory
-
A class is like a factory that creates objects of that class
-
We ask a class to create an object by using the keyword:
-
new
-
-
We can also ask the class to initialize the object
- and pass data to help initialize it

basic terminology
-
Object
- Usually a person, place or thing (a noun)
-
Method
- An action performed by/on an object (a verb)
-
Attribute
- Description of objects in a class
-
Class
- A category of similar objects
- Does not hold any values of the object’s attributes
5 minutes break
Clock class abstraction
-
A Clock represents a 12-hour clock
-
Its internal state includes: hour, minute, second
-
Its interface allows telling the clock that a second has elapsed and querying the clock for the time:

Structure of clock class

Constructors
-
Objects must be initialized before use.
-
We must specify what is the initial state of the object before we can use it.
-
- Space for holding the object state data is only allocated when the object is constructed.
- We specify the way an object is initialized using a constructor, which is a special method invoked every time we create a new object.
- The name of the constructor is always identical to the class name
clock constructor

"new" operator (1)
-
"new" creates a new object from
specified type:
-
new String();
-
new Book();
-
"new" operator (2)
-
Returns the reference to the created object
-
String s = new String();
-
Dog d = new Dog();
-
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
-
-
Primitive types are not referenced:
- new int();

object references
-
When you declare an object, you declare its reference:
- String s;
- Book b;
-
Exception:
- Primitive types
-
Primitive types are not actually objects
- They cannot have references
create objects
- "String str;" will not create an object
- It just creates a reference
-
You cannot use “str” variable, “str” is null
- null value in java
- You should connect references to real objects
-
How to create objects?
- new
- Or static value in case of String: String str = “Hello”;
Time for another Demo?
Copy of CMPS12A - Lecture 8
By Narges Norouzi
Copy of CMPS12A - Lecture 8
- 555



