Lecture 9

Fall 2018
Narges Norouzi
what's a class made of?
-
Members of a class:
-
Attributes or Fields (instance variables, data)
-
For each instance of the class (object), values of attributes can vary, hence they are instance variables
-
-
Methods (instance methods)
-
-
Person class
-
Attributes: name, address, phone number
-
Methods: change address, change phone number
-
-
Alice object
-
Name is Alice, address is ...
-
Constructors
-
Objects must be initialized before use.
-
We must specify what is the initial state of the object before we can use it.
-
- Space for holding the object state data is only allocated when the object is constructed.
- We specify the way an object is initialized using a constructor, which is a special method invoked every time we create a new object.
- The name of the constructor is always identical to the class name
clock constructor

"new" operator
-
"new" creates a new object from
specified type:
-
new String();
-
new Book();
-
Invoking clock constructor

Passing parameters
-
When a parameter is passed, a copy of the value is made and assigned to the formal parameter:

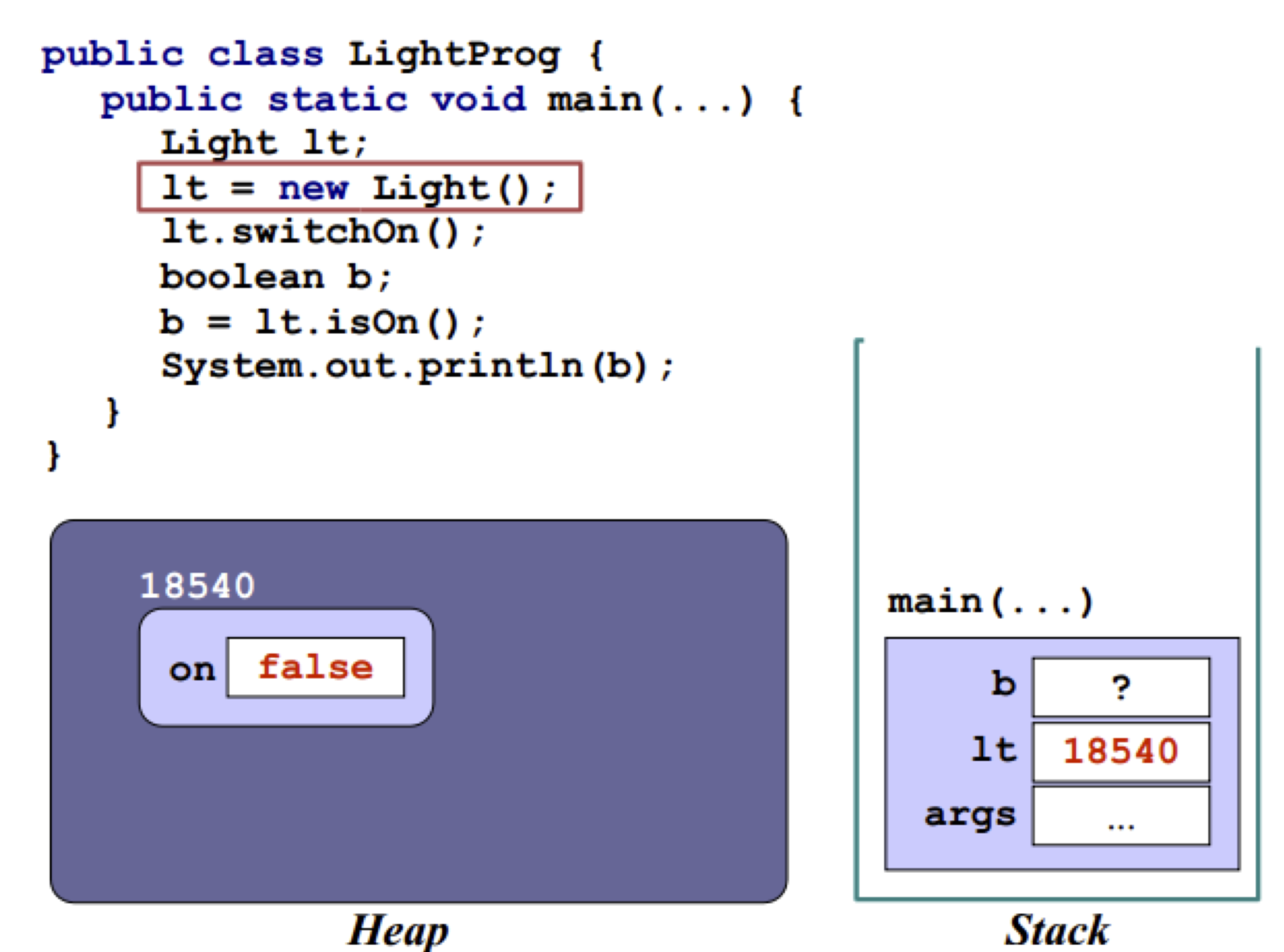
Memory management in heap





5 minutes break
Instance methods
secondelapsed() method

method context
-
The getHours() and secondElapsed() methods are instance methods, which means they act on a particular instance of the class
-
They cannot be invoked “out of the blue”. They must act on a particular object
-
An instance method is executed in the context of the object it acts upon.

method settime()

Testing clock class

variable scope
-
Variables may be declared in:
-
Class – state variables
-
Method/constructor – local variables (and parameters)
-
Inner block of a method – also local variables
-
- A variable is recognized throughout the block in which it was defined.
- Local variables are allocated when the method is entered and freed when the method exits.
- The same name may be used in different scopes, and refer to totally different things.
- If the same name is used in an outer and inner scope, then the inner scope definition “hides” the outer one.
the "this" reference
-
When appearing inside an instance method, the “this” keyword denotes a reference to the object that the method is acting upon.
-
The following are equivalent:


Using same names for parameters & fields
-
It is usually a bad practice to use the same name for a state variable and a local variable or parameter.
-
Exception: parameters that correspond to fields

Zybooks chapters we covered
-
Chapter 7: Objects and Classes
-
section 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.6, 7.9, 7.10, 7.11
-
-
Zybooks chapters we'll cover next
-
Chapter 10: Inheritance
-
Sections 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4
-
Assignment 3 Review
Copy of CMPS12A - Lecture 9
By Narges Norouzi
Copy of CMPS12A - Lecture 9
- 422



